Fixed-Point Notebook
Est. read time: 1 minute | Last updated: March 02, 2026 by John Gentile
Contents
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from rfproto import sig_gen, plot
Rounding Techniques
bitwidth = 16
N = bitwidth - 1
num_tests = 10000
MIN_VAL = -2**N
MAX_VAL = (2**N) - 1
shift_err = np.zeros(num_tests)
halfup_err = np.zeros(num_tests)
tozero_err = np.zeros(num_tests)
conv_err = np.zeros(num_tests)
def err_mag(x, ref):
return (ref - (x / 2**N))
for i in range(num_tests):
a = random.randint(MIN_VAL, MAX_VAL)
b = random.randint(MIN_VAL, MAX_VAL)
# full-width integer product, before any rounding/scaling scheme
c = a * b
# Floating-point comparison
a_fp = 1.0 * a / 2**N
b_fp = 1.0 * b / 2**N
c_fp = a_fp * b_fp
# Truncation: Simple bit shift >>
c_shift = c >> N
shift_err[i] = err_mag(c_shift, c_fp)
# Round half up: basic scheme, similar to mulhrs AVX intrinisc
# Truncate to N+1 bits, += 1, truncate down to final size >> 1
# Better than raw truncation, but still some bias...
c_halfup = ((c >> (N-1)) + 1) >> 1
halfup_err[i] = err_mag(c_halfup, c_fp)
# Round towards 0:
c_to_0 = ((c >> (N-1)) + 1) >> 1 if (c < 0) else ((c >> (N-1)) - 1) >> 1
tozero_err[i] = err_mag(c_to_0, c_fp)
# Convergent rounding
# default rounding mode used in IEEE 754 FP computing functions
# from https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug901-vivado-synthesis/Rounding-to-Even-Verilog
multadd = c + 32768
c_conv = multadd >> N
if ((multadd & 0xFFFF) == 0): # pattern detect DSP48
c_conv &= 0xFFFFFFFE
#print(f"{c_shift} {c_conv}")
conv_err[i] = err_mag(c_conv, c_fp)
schemes = [
"Shift",
"Half-Up",
"Towards-Zero",
"Convergent",
]
means = [
abs(np.average(shift_err)),
abs(np.average(halfup_err)),
abs(np.average(tozero_err)),
abs(np.average(conv_err)),
]
stds = [
np.std(shift_err),
np.std(halfup_err),
np.std(tozero_err),
np.std(conv_err),
]
bar_width = 0.5
spacing = 1.25
n_sch = len(schemes)
x_means = np.linspace(0, spacing*(n_sch-1), n_sch)
x_stds = [x + bar_width for x in x_means]
x_lbls = [x + bar_width/2 for x in x_means]
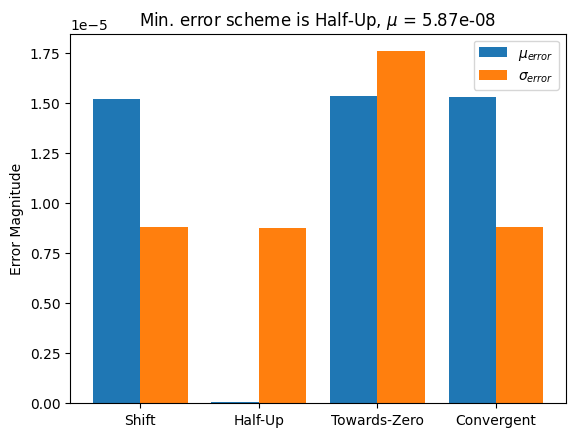
idx_min = np.argmin(means)
plt.bar(x_means, means, width=bar_width, label = r'$\mu_{error}$')
plt.bar(x_stds, stds, width=bar_width, label = r'$\sigma_{error}$')
plt.xticks(x_lbls, schemes)
plt.ylabel('Error Magnitude')
plt.title(r'Min. error scheme is {0}, $\mu$ = {1:.2e}'.format(schemes[idx_min], means[idx_min]))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
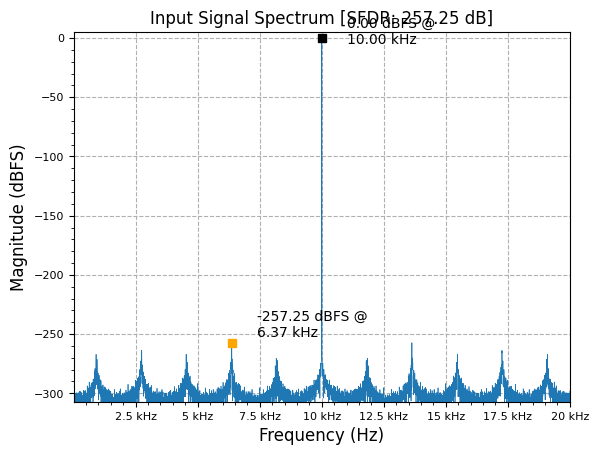
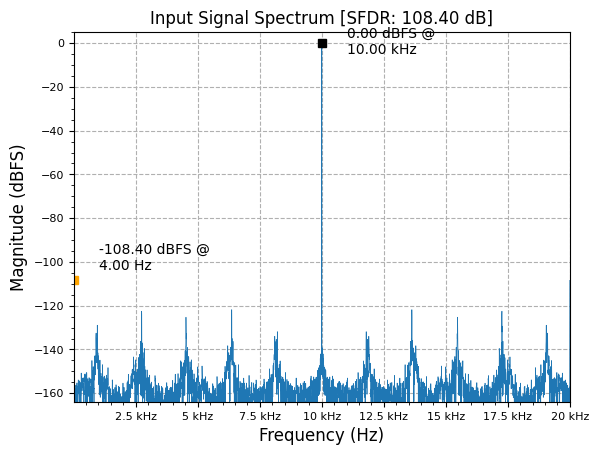
input_sig = sig_gen.cmplx_dt_sinusoid(2**20, 10000, 40000, 10000).real
floor_sig = np.floor(input_sig / 8)
plot.spec_an(input_sig, 40000, "Input Signal Spectrum", scale_noise=True, norm=True)
plot.spec_an(floor_sig, 40000, "Input Signal Spectrum", scale_noise=True, norm=True)
plt.show()
References
- Rounding to Nearest Integer - Wikipedia
- Convergent Rounding LSB Correction Technique - Vivado UG901
- Rounding Numbers without Adding a Bias