TX Pulse Shaping & Matched Filters
Est. read time: 1 minute | Last updated: February 16, 2026 by John Gentile
Contents
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import signal
from rfproto import filter, modulation, plot, sig_gen
Matched Filtering
- The why (bandwidth and power amplifiers) -> https://dsp.stackexchange.com/questions/41130/envelope-behavior-difference-between-qpsk-oqpsk-and-pi-4-qpsk
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raised-cosine_filter
# CCSDS OQPSK SRRC rolloff=0.5: https://public.ccsds.org/Pubs/413x0g3e1.pdf
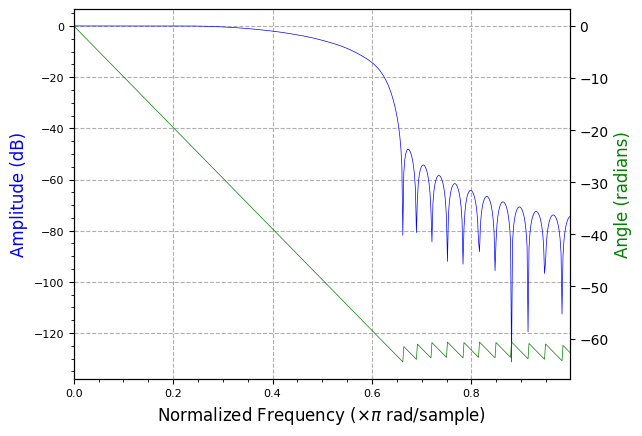
rrc_test = filter.RootRaisedCosine(17.225e6, 7.5e6, 0.5, 63)
# The matched filter is a time-reversed and conjugated version of the signal
# NOTE: this is moot for a uniform, real filter...
rrc_mf = np.conj(rrc_test[::-1])
plot.filter_coefficients(rrc_mf)
plt.show()
plot.filter_response(rrc_mf)
plt.show()
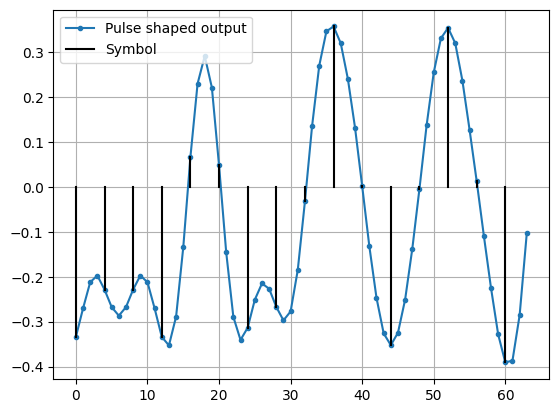
# simulate random binary input values
num_symbols = 2400
num_disp_sym = 16
sym_rate = 1e6 # Baseband symbol rate
# Generate random QPSK symbols
rand_symbols = np.random.randint(0, 4, num_symbols)
L = 4 # Upsample ratio (Samples per Symbol)
fs = L * sym_rate # Output sample rate (Hz)
rolloff = 0.25 # Alpha of RRC
num_filt_symbols = 6 # Symbol length of RRC matched filter
qpsk_tx_filtered = sig_gen.gen_mod_signal(
"QPSK",
rand_symbols,
fs,
sym_rate,
"RRC",
rolloff,
num_filt_symbols,
)
# Show time domain aspects of interpolation & pulse-shapinp
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(np.real(qpsk_tx_filtered[:num_disp_sym * L]), '.-', label='Pulse shaped output')
num_taps = 64
for i in range(num_disp_sym):
if not i:
plt.plot([i*L,i*L], [0, np.real(qpsk_tx_filtered[i*L])], color='k', label='Symbol')
else:
plt.plot([i*L,i*L], [0, np.real(qpsk_tx_filtered[i*L])], color='k')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
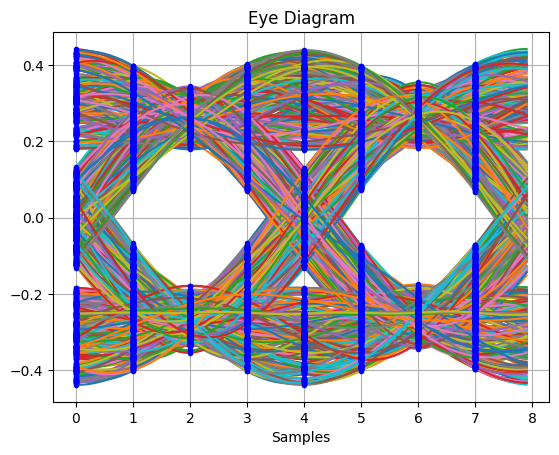
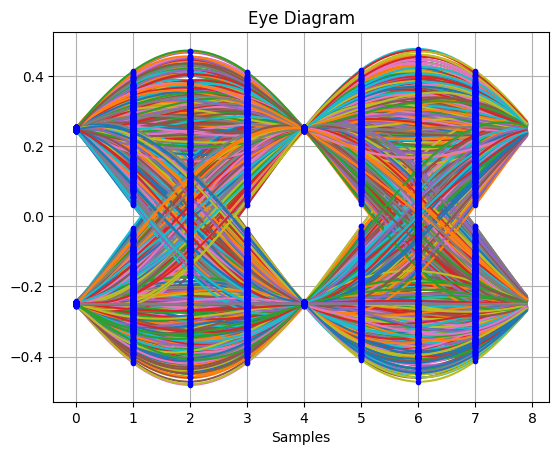
_,_ = plot.eye(qpsk_tx_filtered.real, L)
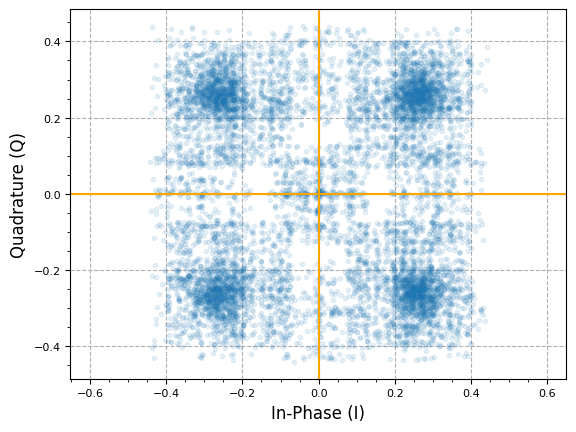
plot.IQ(qpsk_tx_filtered, alpha=0.1)
plt.show()
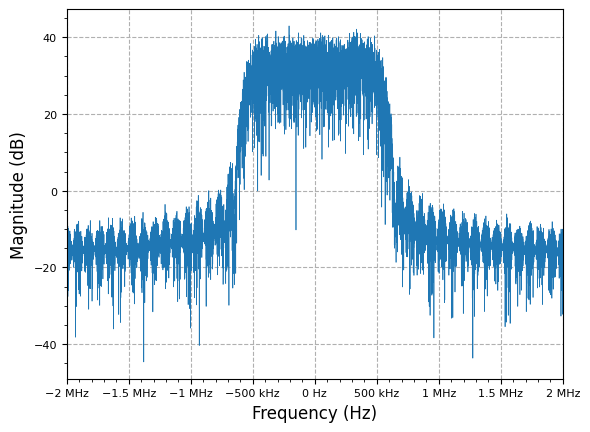
plot.spec_an(qpsk_tx_filtered, fs=fs, fft_shift=True, show_SFDR=False, y_unit="dB")
plt.show()
# Pass transmitted waveform through same RRC (matched filter)
rrc_coef = filter.RootRaisedCosine(L * sym_rate, sym_rate, rolloff, 2 * num_filt_symbols * L + 1)
rx_shaped = signal.lfilter(rrc_coef, 1, qpsk_tx_filtered)
# don't plot begining samples while starting filter convolution process
transient = (len(rrc_coef)//2 + 1) * L
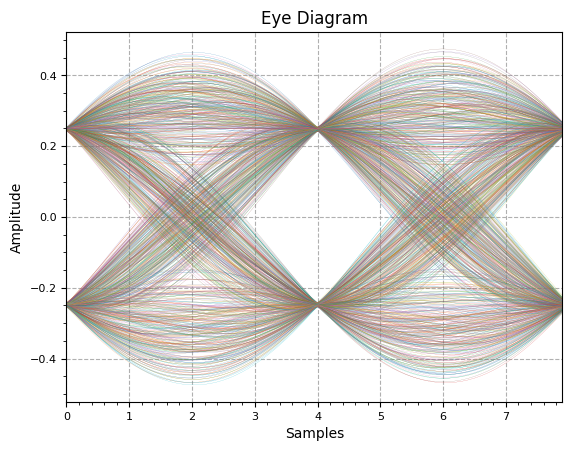
_,_ = plot.eye(rx_shaped.real[transient:], L )
# adjust for best EVM, similar to slicer
timing_offset = 4
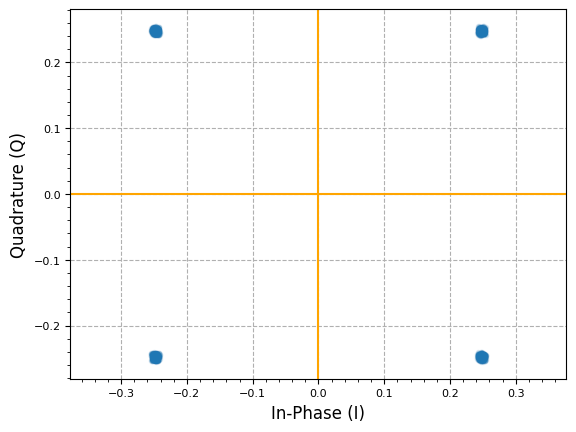
plot.IQ(rx_shaped[transient + timing_offset::4], alpha=0.1)
plt.show()
Derivative Matched Filter (DMF)
n_fft = 2048
freq_bins = np.linspace(-L/2, L/2, n_fft)
H_rrc = np.fft.fft(rrc_coef, n_fft)
H_dmf = 1j* 2 * np.pi * np.fft.fftfreq(n_fft) * L * H_rrc
dmf_full = np.fft.ifft(H_dmf)
dmf = np.real(dmf_full[:len(rrc_coef)])
#dmf /= np.max(np.abs(dmf))
Y_rrc = 20.0 * np.log10(np.abs(np.fft.fftshift(H_rrc)))
Y_dmf = 20.0 * np.log10(np.abs(np.fft.fftshift(np.fft.fft(dmf, n_fft))))
plt.figure()
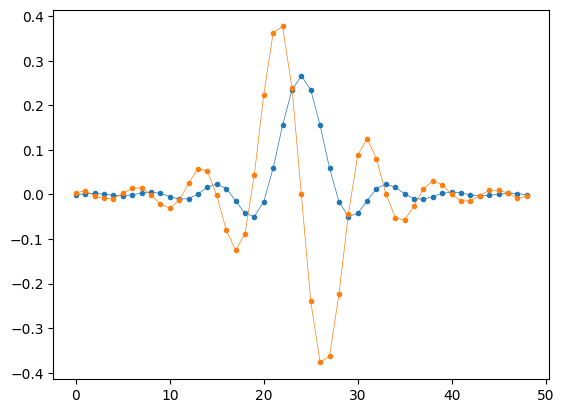
plt.plot(rrc_coef, '.-', linewidth=0.5)
plt.plot(dmf, '.-', linewidth=0.5)
plt.show()
plt.figure()
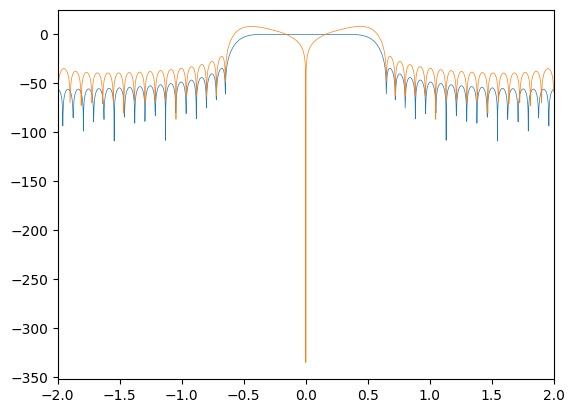
plt.plot(freq_bins, Y_rrc, linewidth=0.5)
plt.plot(freq_bins, Y_dmf, linewidth=0.5)
plt.margins(x=0)
plt.show()
References
- Digital Pulse-Shaping Filter Basics - ADI AN-922
- Root Raised Cosine (RRC) Filters and Pulse Shaping in Communication Systems - NASA
- Frequency Response of RRC Filter - DSP Stack Exchange
- Raised Cosine Filtering - MATLAB
- Raised-Cosine Filter - Wikipedia
- The care and feeding of digital, pulse-shaping filters
- Matched Filter - Wikipedia