Distributed Computing
Est. read time: 2 minutes | Last updated: March 09, 2026 by John Gentile
Contents
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
- Virtualization and Containers
- Cloud
- High-Performance Network Programming
- References
Architectures and design patterns for systems that are data intensive, as well as distributed computing systems. For a great overview, and impetus for AWS, see Amazon’s Distributed Computing Manifesto.
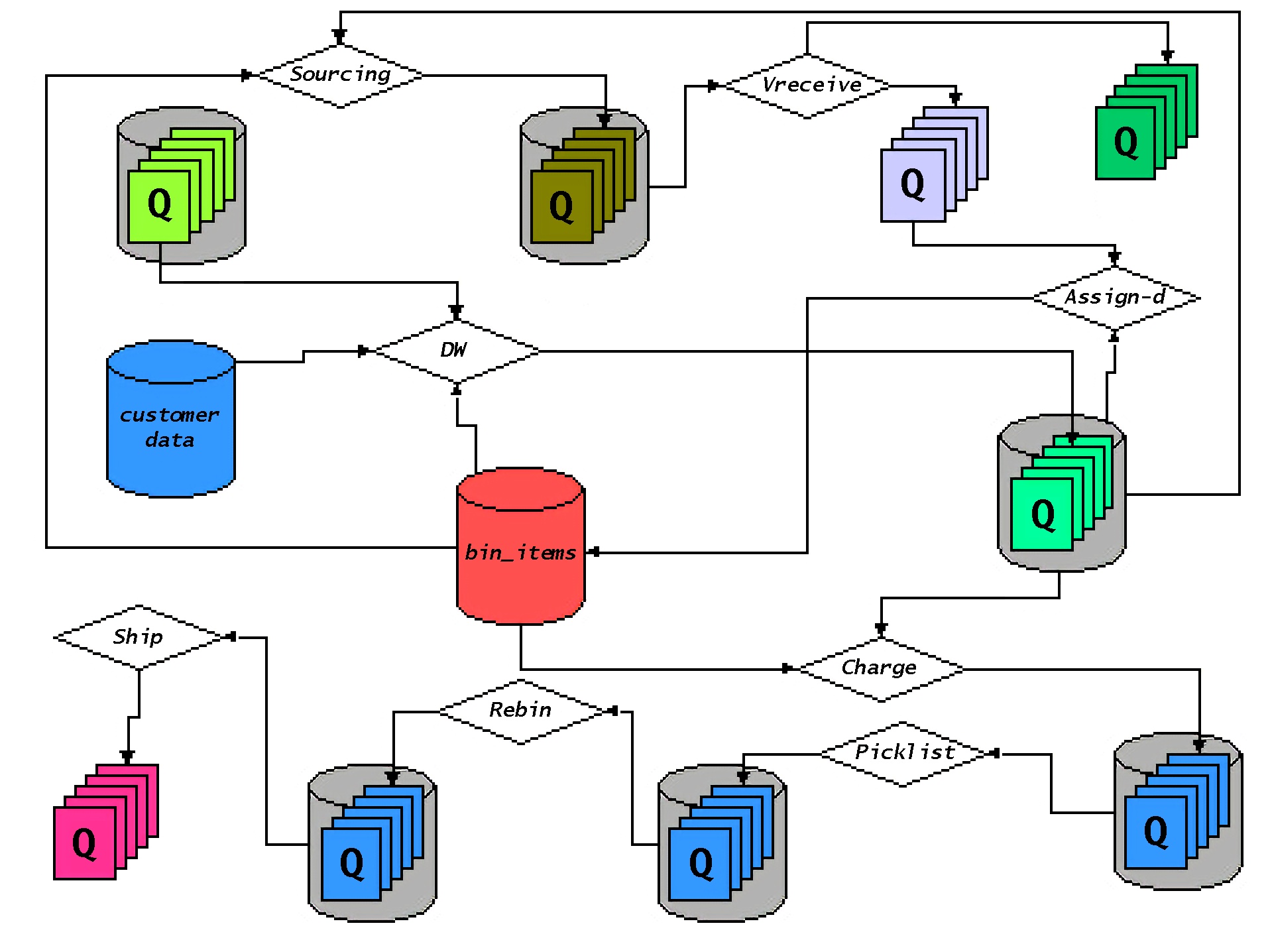
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
Debug/Tools
curl can be used to debug REST APIs like:
- Displaying response and headers with
$ curl -v http://www.example.com/api/ping - PUT method with
$ curl -X PUT -d 'name=Sugar&category_id=3' http://www.example.com/api/products - Use authentication with a token like
$ curl -H "Authorization: Bearer b1094abc0-54a4-3eab-7213-877142c33fh3" http://example.com/api/resource - Show the HTTP response code with
$ curl -I http://www.example.com/ - And much, much more like in everything curl
Virtualization and Containers
Virtual Machines (VM)
Containers
Useful Docker Commands
- Restart last container created:
docker start $(docker ps -ql)- Reattach terminal & stdin to last:
docker attach $(docker ps -ql)
- Reattach terminal & stdin to last:
- List currently running Docker instances:
docker ps -a - Stop all containers:
docker kill $(docker ps -aq) - Delete all containers, including its volumes they use:
docker rm -vf $(docker ps -aq) - Delete all docker images:
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)- NOTE: you should remove all containers before removing all the images from which the containers were created.
- Delete everything (removing all unused containers, volumes, networks, images, etc.) and reclaim disk space (essentially remove everything!), use:
docker system prune -a --volumes
References
Cloud
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
High-Performance Network Programming
- Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)
- How to receive a million packets per second
- High Performance Browser Networking by Ilya Grigorik
- A Cloud-Optimized Transport Protocol for Elastic and Scalable HPC - Paper on AWS Scalable Reliable Datagram (SRD)
Packet FEC in lieu of Retransmission
When latency is key (can’t wait/block for packet loss) in lossy networks (e.x. WAN, intermittent links, etc.), Forward Error Correction (FEC) techniques (similar to those used at the physical layer) can be applied at the network layer. For instance in SD-WAN FEC, lost packets can be recovered on a link by sending extra “parity” packets for every $N$ packets. See more details on Information Theory.
References
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications
- Fly.io Gossip Glomers: a series of distributed systems challenges
- Readings in Database Systems, 5th Edition
- Mastering Chaos - A Netflix Guide to Microservices - YouTube
- Google - Site Reliability Engineering
- The Amazon Builders Library
- Time, Clocks and the Ordering of Events in a Distributed System - Microsoft Research
- Foundational distributed systems papers
- MIT 6.824 Distributed Systems (Spring 2020) - YouTube
- JohnCrickett/SystemDesign: Useful resources on distributed system design.
- theanalyst/awesome-distributed-systems: A curated list to learn about distributed systems
- onurakpolat/awesome-bigdata: A curated list of awesome big data frameworks, ressources and other awesomeness.
- Testing Distributed Systems- Curated list of resources on testing distributed systems
- Fallacies of distributed computing - Wikipedia
- The Architecture of Open Source Applications
- System Design Interview - YouTube
- You Want Modules, Not Microservices
- Death By a Thousand Microservices
- Database Fundamentals
- 15-445/645 Intro to Database Systems (Fall 2019) - YouTube